Semester 1: Foundation of Basic Science
Case 1: Chemistry of Life
Obj 2: Chemical Bond & its Characteristics
![Polar covalent bond [Credits : Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.]](http://cache-media.britannica.com//eb-media/04/96904-004-C880B85D.gif)
- < 1.7 difference electronegativity (less ionic)
 2) Ionic (electrostatic forces)
2) Ionic (electrostatic forces)
- a bond between metal (low e) + non metal (high e) by electron transfer
- > 1.7 difference electronegativity (more ionic)
- cation (+ ion) / anion (- ion)
 3) Metallic
3) Metallic
- a bond between metal + metal in crystal lattice
- have low ionization energy (so electron move around n act as cement that hold metal ions)
- lustrous / malleable / ductile


3)Hydrophobic Attraction / Interaction (Molecule - Ion Interaction)
-Interaction / between non-polar side chain molecule / and other non-polar side chain molecule / which tend to aggregate minimizing surface area exposed to water (to avoid water molecules) / allowing these molecules to associate with each other in aqueous environment
Case 1: Chemistry of Life
Obj 2: Chemical Bond & its Characteristics
Chem Bonds =divided into two (Intramolecule / Intermolecule)
- Intramolecular bond
![Polar covalent bond [Credits : Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.]](http://cache-media.britannica.com//eb-media/04/96904-004-C880B85D.gif)
1) Covalent
- a bond between non metal + non metal by sharing electron to achieve stable electronic configuration
- electron shared = no of bonds- < 1.7 difference electronegativity (less ionic)
- Polar = when atom is more electronegative than another
- Non-polar = when electron equally shared

- a bond between metal (low e) + non metal (high e) by electron transfer
- > 1.7 difference electronegativity (more ionic)
- cation (+ ion) / anion (- ion)

- a bond between metal + metal in crystal lattice
- have low ionization energy (so electron move around n act as cement that hold metal ions)
- lustrous / malleable / ductile
- Intermolecular Bond

1) Hydrogen bond
- electrostatic attraction between an electronegative atom (O / N) + a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to 2nd electronegative atom
- increase electronegativity of atom bounded to hydrogen = increase bond strength
-can be either intermolecular o intramolecular

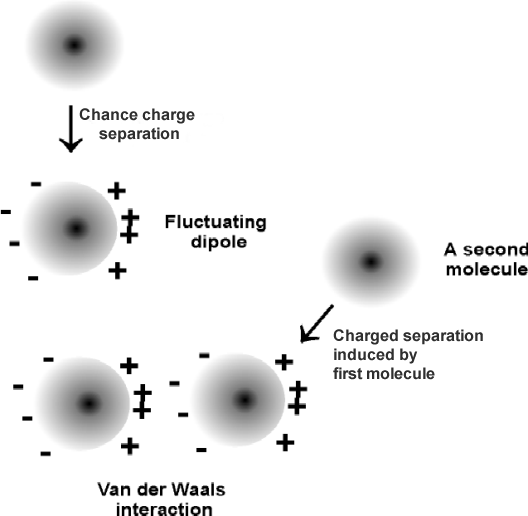
2) Van der Waals
-short-range forces / between molecules or parts of molecules / where atoms attract when they are at certain distance / and repel when the atoms approach (tendency to maintain distance)
-more significant when (increase pressure / decrease temperature)
3)Hydrophobic Attraction / Interaction (Molecule - Ion Interaction)
-Interaction / between non-polar side chain molecule / and other non-polar side chain molecule / which tend to aggregate minimizing surface area exposed to water (to avoid water molecules) / allowing these molecules to associate with each other in aqueous environment

0 comments:
Post a Comment