Semester 1: Foundation of Basic Science
Case 1: Chemistry of Life
Obj 3: Structure of DNAs & its Functions
DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid

- DNA STRUCTURE
= Long chain of nucleotide

Nucleotide - composed of
- Phosphate Group (PO4)
- 5C Sugar (Ribose - RNA / Deoxyribose - DNA)
- Nitrogenous Base (Purine -2 ring(AG) / Pyrimidine-1 ring(TCU)

Basic Structure Of Nucleotide

Difference between Ribose and Deoxyribose of 5C Sugar
Difference between Purine & Pyrimidine of Nitrogenous Base

Difference between Nucleoside and Nucleotide
Primary Structure-Double stranded Helix
-the 2 strands are anti-parallel
-always read 5' to 3'
-polymers linked 3' to 5' by phosphodiester bridges
-bonds between
- polymers (phosphate & sugar) - phosphodiester bridges
- sugar & base - (purine =B-N9-glycosidic bond / pyrimidine =B-N1-glycosidic bond)
- base & base - hydrogen bond

Phosphodiester Bond (Phosphate-Sugar)

Glycosidic Bond (Sugar-Base)

Hydrogen Bond (Base-Base)
A-T (2) / G-C (3)
Secondary Structure-sugar-phosphate backbone outside
-Bases (hydrogen bonded) inside
-Base-pairing rule { A-T (2) / G-C (3) }
- DNA FUNCTIONS
- Storage information
- Replication
- Access of infomation for protein synthesis
-Carrying the genetic information through generation
Functions of Nucleotides
- Nucleoside 5'-triphosphates are carriers of energy, energy stores
- Forming a portion of several important coenzymes such as NAD+, NADP+, FAD and coenzyme A
- activated intermediates in numerous biosynthetic reactions, as SAM in glycoprotein synthesis
- Cyclic nucleotides are signal molecules (second messenger) and regulators of many aspects of cellular metabolism
- ATP is central to energy metabolism
- GTP drives protein synthesis
- CTP drives lipid synthesis
- UTP drives carbohydrate metabolism
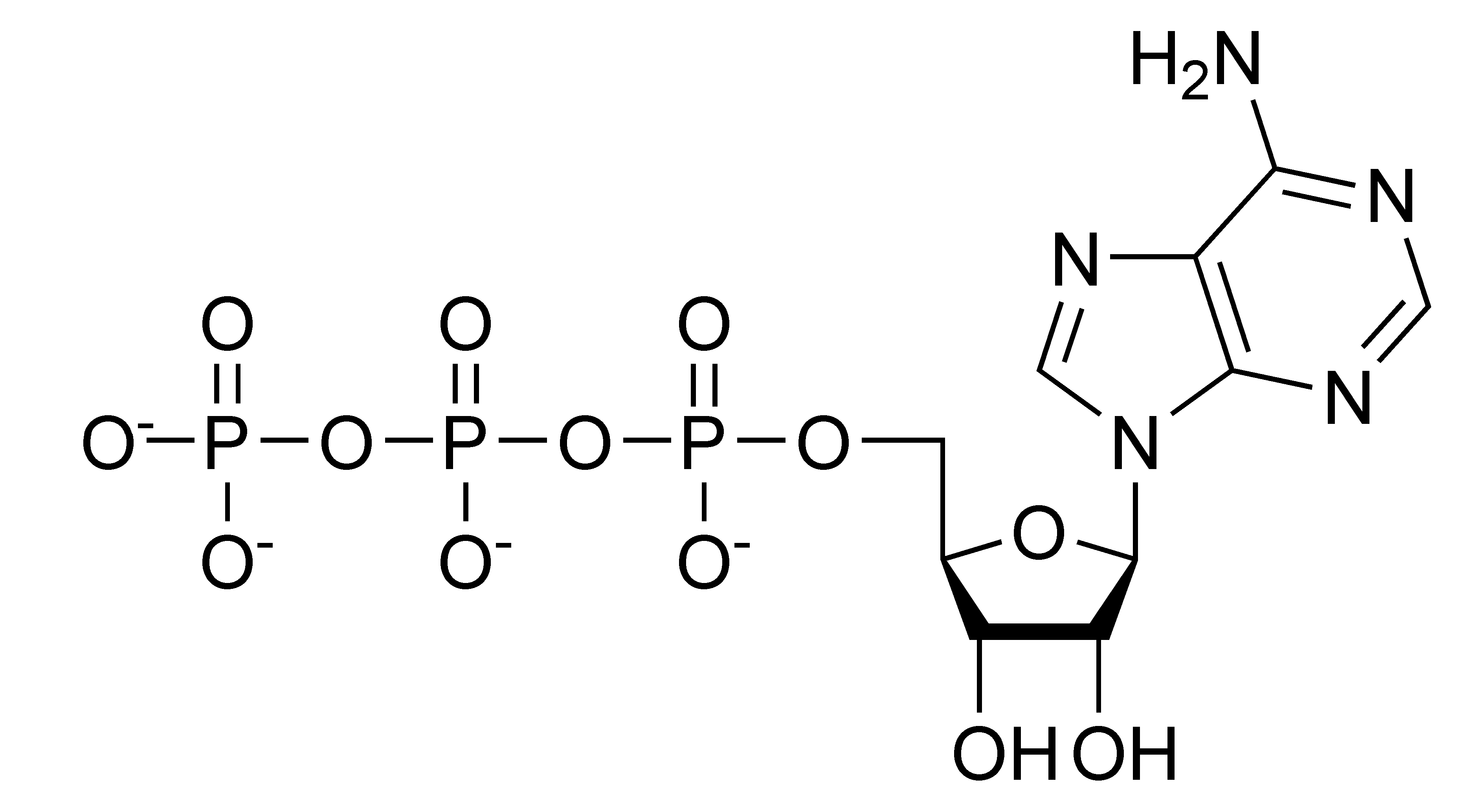
ATP

GTP

CTP

UTP

0 comments:
Post a Comment